
ASX Reference Manual
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Installation and Usage
- Coding Conventions
- Compiling applications that use the ASX interface
- Functions
- Example code
- Porting Applications from PCXTools
- Deprecated
Introduction
ASX is an audio API designed to work on both Windows and Linux operating systems. It is "high level", in that unlike say the Windows WAVE or Direct Sound APIs, which are "buffer based", it deals with audio files.
At a lower level, ASX supports the AudioScience HPI API (Windows and Linux) as well as WAVE and DirectSound (Windows) and ALSA (Linux).
The API is a C function library. This means it can be used from many languages including C, C++, C#, Java, Visual Basic and Delphi.
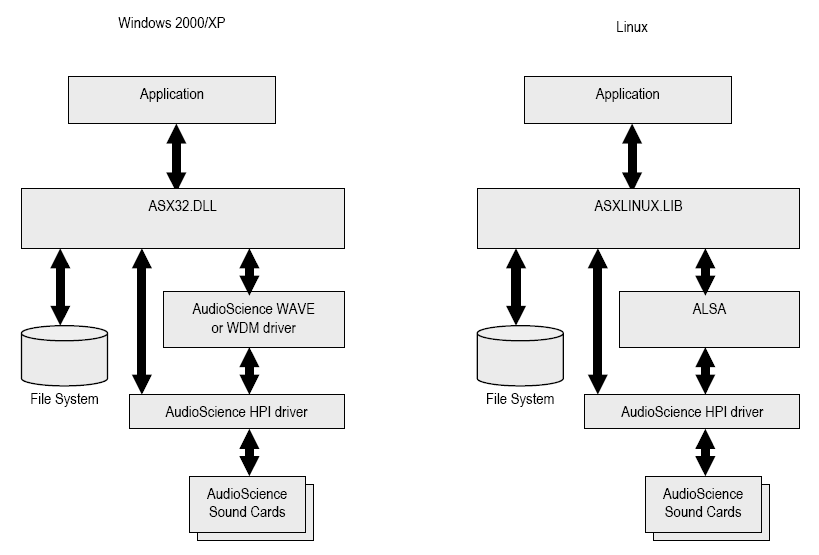
Installation and Usage
Windows
- Make sure you have an AudioScience WAVE,WDM or Combo driver installed and working with at least one audio adapter. The driver install will install both ASX32.DLL (and optionally ASX64.DLL)which implements the ASX interface documented here and ASICTRL.EXE which is a Windows application that uses the ASX interface to control ASI adapters.
- Obtain the ASX SDK executable file from the applications section of the AudioScience web site (<http://www.audioscience.com/>). The file is named ASX_SDK_WIN_XXXXX.EXE, where XXXXX is the version number.
- Run the ASX_SDK_WIN_XXXXX.EXE application to install asx.h, code examples and asx32.lib.
Linux
ToDo
Compiling applications that use the ASX interface
The various interface files required to interface with asx32.dll are typically installed in c:\Program Files\AudioScience\ASX\lib directory.
Applications can make use of asx.h and asxstring.h header files and should link against asx.32lib.
Debugging ASX calls under Windows
ASX ships with the capability of outputting debug information to a Third Party debug viewer.
DbgView should be used to display the debug messages. It is available from Microsoft and the simplest method of locating it is to just Google "DbgView". Download and install this on the PC you wish to test on.
The appliction being debugged should call ASX_System_SetMessageLogging to turn on error logging. Setting the error level to asxMSG_LOGGING_DEBUG will record all ASX calls and output other information as well.
ASX Object Model
In ASX, the underlying audio hardware is grouped into "adapters". An adapter is typically a soundcard (i.e. AudioScience ASI6114).
Each adapter has a "mixer". The mixer contains source and destination "nodes". A node represents a point at which audio comes in (source) or leaves (destination) the mixer.
Source nodes include:
- playback streams from the computer (usually from a file).
- physical audio inputs like an analog line input or AES/EBU input.
Destination nodes include:
- record streams to the computer (usually to a file).
- physical audio outputs like an analog line output or AES/EBU output.
Nodes are attached to "controls" which contain functionality to process the audio streams passing through them. Examples of controls include:
- Player control to play audio from a file on the computer.
- Recorder control to record audio to a file on the computer.
- Meter control to observe the audio signal's peak and RMS values.
- Volume control to alter the audio level.
- Channel Mode control to swap left and right channels on a stream.
- Level control to set the physical input and output levels on an analog node.
- AES/EBU control, which allows access to the channel status and user data.
The following diagram shows how ASX models a simple sound card:
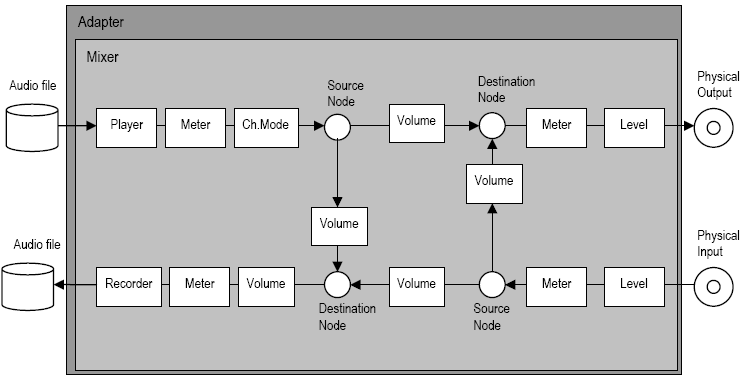
Coding Conventions
Method names
- 1st letters are ASX_ int uppercase, i.e ASX_Adapter_GetMixer()
Variable names use Hungarian notation, i.e.
- int - prefix with "n", i.e int nIndex
- long - prefix with "l", i.e long lIndex
- unsigned long - prefix with "dw", i.e unsigned long dwSampleRate;
- float - prefix with "f", i.e float fNumber;
- pointer - prefix with "p", i.e int* pnIndex
- reference - prefix with "r", i.e int& rnIndex
- string (char array) - prefix with "sz", i.e char szString[40];
- global var - prefix with "g", i.e int gnIndex
- static var - prefix with "s", i.e int snIndex
- member var - prefix with "m", i.e int mnIndex
- enum - prefix with "asx", then all capitals with "_" separators, i.e. asxERROR_INDEX_OUT_OF_RANGE
Return conventions All functions return ASX_ERROR which equals 0 on success and non-zero on error.
 1.7.3
1.7.3